网络请求是开发APP必不可少的一部分,比如获取用户订单数据,获取商品列表,提交表单等等都离不了网络请求,那么在Flutter中如何进行网络请求呢?
基于Http实现网络操作
- 如何用Http库做get请求?
- 如何用Http库做post请求?
- 如何将Response转换成Dart object?
- 如何将请求结果展示在界面上?
Flutter官方推荐我们在Flutter中用Http进行网络请求。
什么是Http?
Http是Flutter社区开发的一个可组合的、跨平台的用于Flutter的网络请求插件。
如何用http库做get请求?
- 在
pubspec.yaml中引入http插件;
- 调用
http.get发送请求;
1
2
| dependencies:
http: <latest_version>
|
1
2
3
| Future<http.Response> fetchPost() {
return http.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
}
|
http.get()返回一个包含http.Response的Future:
- Future:是与异步操作一起工作的核心Dart类。它用于表示未来某个时间可能会出现的可用值或错误;
http.Response:类包含一个成功的HTTP请求接收到的数据;
如何将Response转换成Dart object?
虽然发出网络请求很简单,但如果要使用原始的Future<http.Response>并不简单。为了让我们可以开开心心的写代码,我们可以将http.Response转换成我们自己的Dart对象。
创建一个CommonModel类
首先,我们需要创建一个CommonModel类,它包含我们网络请求的数据。它还将包括一个工厂构造函数,它允许我们可以通过json创建一个CommonModel对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class CommonModel {
final String icon;
final String title;
final String url;
final String statusBarColor;
final bool hideAppBar;
CommonModel({this.icon, this.title, this.url, this.statusBarColor, this.hideAppBar});
factory CommonModel.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return CommonModel(
icon: json['icon'],
title: json['title'],
url: json['url'],
statusBarColor: json['statusBarColor'],
hideAppBar: json['hideAppBar'],
);
}
}
|
将http.Response转换成一个CommonModel对象
现在,我们将更新fetchPost函数以返回一个Future。为此,我们需要:
- 使用dart:convert package将响应内容转化为一个json Map;
- 使用fromJson工厂函数,将json Map 转化为一个CommonModel对象;
1
2
3
4
5
| Future<CommonModel> fetchPost() async {
final response = await http.get('http://www.devio.org/io/flutter_app/json/test_common_model.json');
final result = json.decode(response.body);
return new CommonModel.fromJson(result);
}
|
如何将请求结果展示在界面上?
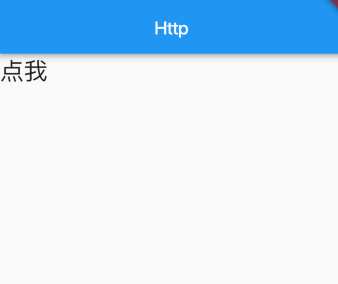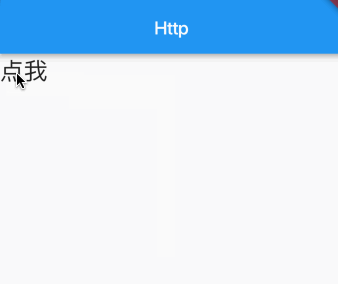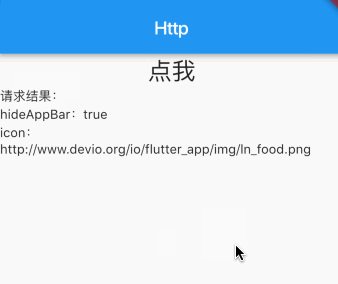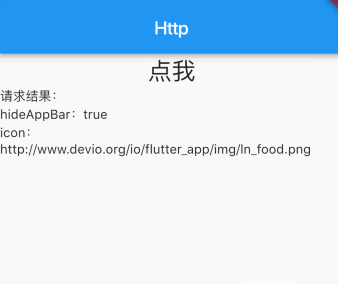
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
String showResult = '';
Future<CommonModel> fetchPost() async {
final response = await http
.get('http://www.devio.org/io/flutter_app/json/test_common_model.json');
final result = json.decode(response.body);
return CommonModel.fromJson(result);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Http'),
),
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
InkWell(
onTap: () {
fetchPost().then((CommonModel value) {
setState(() {
showResult =
'请求结果:\nhideAppBar:${value.hideAppBar}\nicon:${value.icon}';
});
});
},
child: Text(
'点我',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 26),
),
),
Text(showResult)
],
),
),
);
}
}
class CommonModel {
final String icon;
final String title;
final String url;
final String statusBarColor;
final bool hideAppBar;
CommonModel(
{this.icon, this.title, this.url, this.statusBarColor, this.hideAppBar});
factory CommonModel.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return CommonModel(
icon: json['icon'],
title: json['title'],
url: json['url'],
statusBarColor: json['statusBarColor'],
hideAppBar: json['hideAppBar'],
);
}
}
|
在上述代码中我们通过fetchPost().then获取Fluter的返回结果,其实Future可以理解为ES5中的Promise。
